A CLI (Command-Line Interface) is a text-based interaction model in which users type commands as text strings to interact with an operating system or a program through a computer. Unlike a TUI, which relies upon a pseudo-graphical form made of characters, an interface that is purely a command-driven one usually would issue output in the form of lines of text upon receiving user instructions.
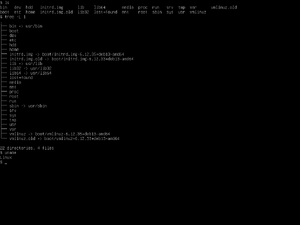
CLIs are often preferred by power users, system administrators, and developers for their efficiency, scriptability, and precise control over system operations. Common examples include:
- Unix/Linux shells (sh, bash, zsh, fish)
- Windows Command Prompt
- PowerShell
- Python's REPL (Read-Eval-Print Loop)
The main advantages of CLIs include:
- Resource efficiency (minimal system requirements)
- Automation capability through scripting
- Remote system administration
- Precise control over system operations
- Speed of execution for experienced users
While CLIs can have a steeper learning curve compared to GUIs (Graphical User Interfaces) or TUIs, they remain fundamental to modern computing, particularly in server administration, software development, and system maintenance.
History
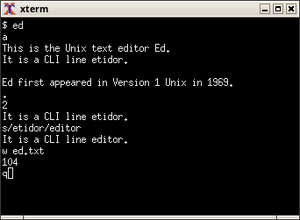
Command-line interfaces emerged in the 1960s with teleprinters like the Teletype Model 33 ASR, which replaced punch cards as the primary means of computer interaction. Early operating systems like Unix and MS-DOS were primarily accessed through CLIs, establishing conventions that persist in modern computing.
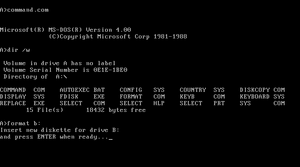
Common Usage
CLI environments typically follow a standard pattern where:
- The system displays a prompt (e.g., "$" for Unix-like systems)
- Users type commands followed by arguments or options
- The system executes the command and displays the output
- The process repeats with a new prompt
